Surgical Suture Characteristics
There are varying types of surgical sutures, and their uses depend on the type of tissue being repaired and the duration of time needed for the suture to stay in place, as well as ease of use. There are absorbable and non-absorbable sutures, monofilament or multifilament, and there are varying materials that comprise sutures. If the suture is braided, it is virtually always coated for an easier penetration.
The chemical composition and the structure of the suture threads, the biocompatibility profile, as well as the intended use and the contraindications of the Golnit sutures are listed in greater detail on the “Instructions of Use”.
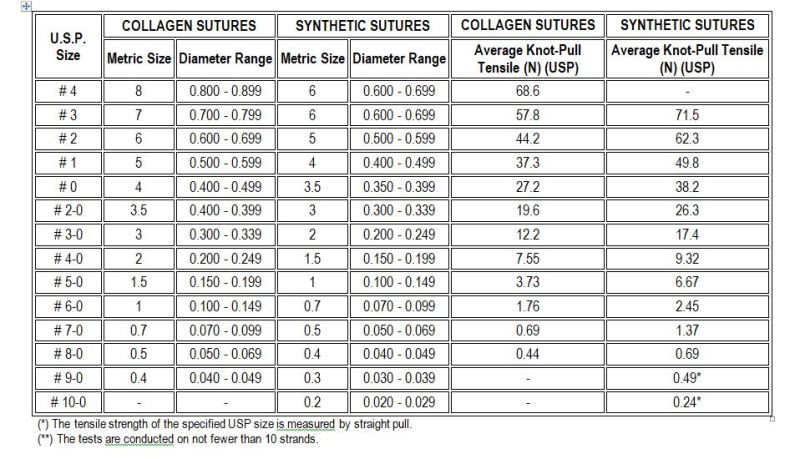
The physical characteristics include size (diameter) of the thread. Golnit sutures follow the USP (United States Pharmacopeia) system and the EP Metric system for suture size (diameter) and tensile strength.
The USP method uses a complex relationship between diameter, tensile strength, and knot security, as listed in the chart below: